Understanding Crooked Teeth from Thumb Sucking
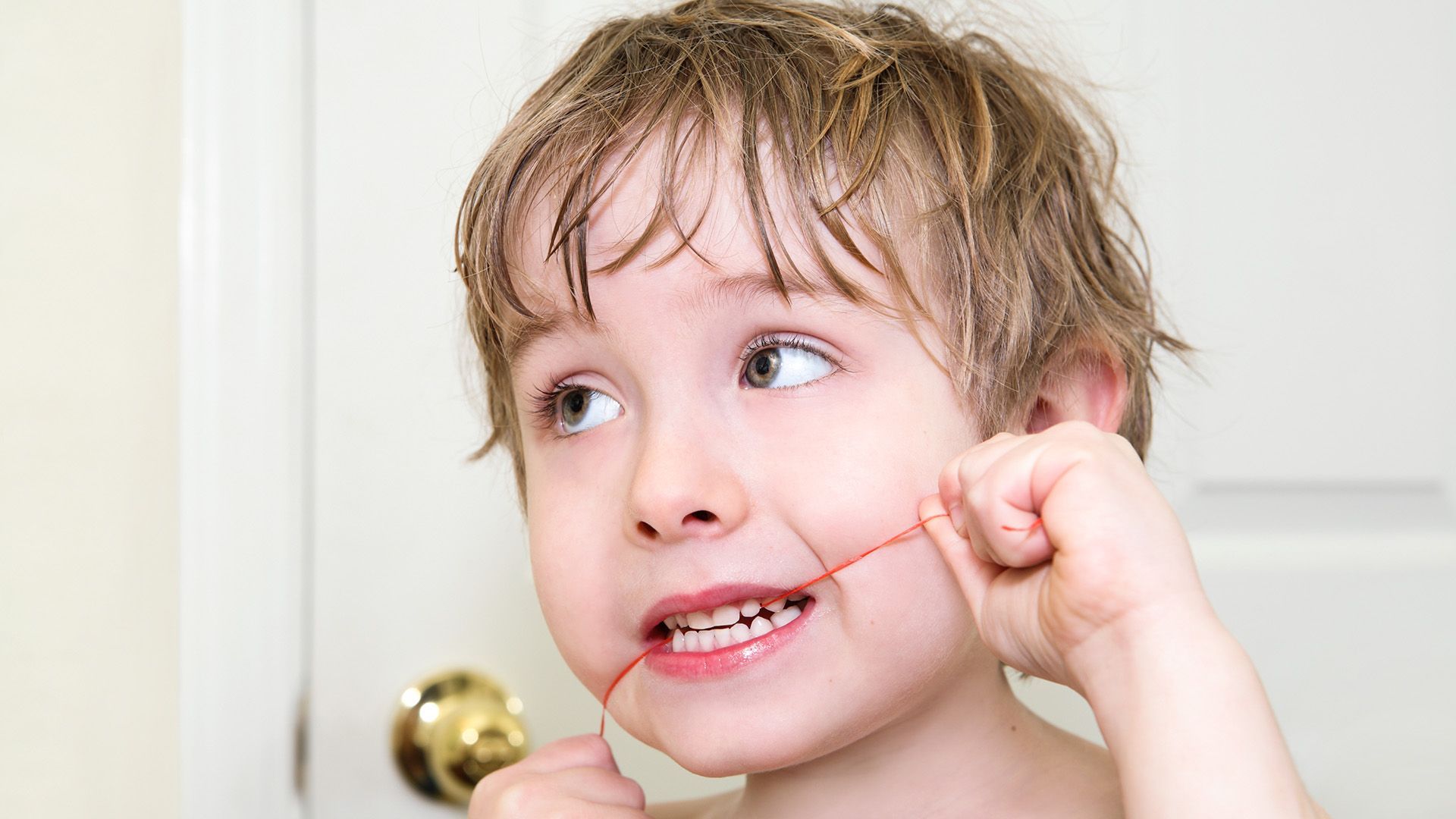
Thumb sucking is a widespread habit among children that offers comfort but can eventually lead to dental problems, such as crooked teeth from thumb sucking. While many children suck their thumbs as a natural reflex or self-soothing mechanism, prolonged thumb sucking can disrupt the alignment of teeth and the development of the jaw, causing misaligned teeth. Understanding how thumb sucking affects dental health is essential for parents who want to ensure their child's oral health. This article delves into the ways thumb sucking leads to dental misalignment, signs that your child’s teeth might be affected, and strategies to help them stop the habit.

How Thumb Sucking Leads to Crooked Teeth
Thumb sucking is a common behavior in infants and young children, providing them with comfort and a sense of security. However, if this habit extends beyond the early years, it can cause significant dental problems, particularly in terms of tooth and jaw alignment. The constant pressure exerted by the thumb on the developing teeth and jaw can lead to various forms of malocclusion.
Prolonged thumb sucking can result in dental issues such as overbites, underbites, and crossbites. An overbite is when the upper front teeth excessively overlap the lower teeth, while an underbite occurs when the lower teeth extend beyond the upper teeth. A crossbite happens when some upper teeth bite inside the lower teeth. These conditions not only impact a child’s appearance but can also hinder their ability to chew and speak properly.
The age at which thumb sucking occurs is critical in determining its impact on dental development. If the habit continues past the age of 4 or 5, the likelihood of permanent dental damage increases. During these years, children’s teeth and jaws are still forming, making them more vulnerable to the detrimental effects of thumb sucking. Early intervention and guidance from dental professionals are essential to mitigate these problems and ensure healthy dental development. Addressing crooked teeth from thumb sucking early can prevent long-term dental issues.
Signs That Thumb Sucking is Affecting Your Child's Teeth
Thumb sucking can lead to noticeable changes in your child's dental health. One of the earliest signs is the appearance of crooked teeth from thumb sucking. Constant pressure from the thumb can push the front teeth out of alignment, leading to a misaligned smile. Parents might observe that their child's teeth are no longer straight or that they overlap in unusual ways.
Besides visual cues, thumb sucking can also alter a child's bite and the spacing of their teeth. Children who suck their thumbs might develop an open bite, where the front teeth do not meet when the mouth is closed. This condition can affect their eating and speaking abilities and might require orthodontic treatment if not addressed promptly.
Additionally, thumb sucking can impact a child's speech and oral function. Prolonged thumb sucking can make it difficult for children to pronounce certain sounds, potentially leading to speech delays. The continuous thumb pressure can also affect the development of the palate, which is crucial for proper speech articulation. Parents should monitor these signs and consult a pediatric dentist to discuss effective strategies for helping their child stop the habit and promote healthy dental development. Observing the condition of teeth after thumbsucking is essential for early intervention.
When to Seek Professional Help
Monitoring your child's dental health is crucial, especially if they have a thumb-sucking habit that could lead to crooked teeth from thumb sucking. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry recommends that children have their first dental evaluation by the age of one or within six months after their first tooth erupts. This early assessment helps identify potential issues, including those related to thumb sucking and its impact on tooth alignment.
Parents should be alert for signs indicating the need for orthodontic intervention. If your child has difficulty biting or chewing, noticeable changes in tooth alignment, or if thumb sucking persists beyond age four, it may be time to consult a dental professional. Other signs include speech difficulties or an open bite, resulting from prolonged thumb sucking.
Consultation with dental professionals can help address the condition of teeth from thumb sucking. Early intervention can prevent long-term issues and ensure your child's smile remains healthy and bright.
Effective Strategies to Help Your Child Stop Thumb Sucking
Helping your child stop thumb sucking can be challenging but ultimately rewarding. Positive reinforcement techniques are an effective approach. Celebrate your child's progress with small rewards for milestones like going a day or a week without thumb sucking. This encouragement can boost their self-esteem and motivate them to continue striving for success.
Introducing alternative comfort methods can also significantly reduce your child's dependency on thumb sucking. Providing comfort objects, such as a favorite stuffed animal or a soft blanket, can help them feel secure without needing their thumb. Engaging in calming activities, like reading together or practicing deep breathing exercises, can serve as healthy distractions.
Engaging with dental professionals for support is invaluable. Experienced
pediatric dentists can assess your child's dental health and discuss the potential impacts of thumb sucking on their teeth alignment. They can also provide tailored strategies to assist your child in overcoming this habit. By working together, you can ensure your child has a healthy, confident smile as they grow. Monitoring the condition of teeth from thumb sucking is crucial for timely intervention.
We believe in the importance of prevention of dental issues at an early age, which helps children have a healthy smile.
USEFUL LINKS
CONTACT US
CURRENT PATIENTS OR PROVIDERS